Biomarker discovery for FAM177A1
When a disease is both rare and new to medicine, the only recourse is research. FAM177A1 Research Fund is excited to shared preliminary results from a foundation-sponsored biomarker discovery project.
In collaboration with
There are only three families in the United States who are living with the cruel reality of a genetically confirmed diagnosis of FAM177A1 (FAM) deficiency. There are without question more FAM families out there, stuck in the invisible purgatory of an interminable diagnostic odyssey. Or yet to be born.
If Jill Hawkins, the founder of the FAM177A1 Research Fund, could install giant neon signs emblazoned with her foundation’s website on every street corner in America, she’d turn up more patients to be sure — but not that many more. No matter how you slice it, FAM deficiency is a tiny rare disease. Outside of a handful of personally devastated families, who even knows it exists?
Overcoming the cold start problem is by no means a unique challenge for families affected by FAM deficiency. All rare disease families must ascend the vertical face of a cliff at the outset of a cure odyssey: convincing (cajoling, really) scientists and clinicians and companies to join their cause instead of competing opportunities, while simultaneously asking (begging, actually) a community of friends, relatives and coworkers to step in as funders of last resort for risky, ground-breaking research projects.
In the absence of basic understanding of the disease — when all you have is a blank slate and blank stares — what are cure-focused, parent-led foundations like FAM177A1 Research Fund supposed to do? As previous n-of-1 medical pioneers have proved, the answers lie within. Literally, coursing through the veins of FAM patients and their families. The ultimate disease expert is the disease itself. The most learned scholar is the parent herself.
As previewed in our last FAM dispatch, Jill in collaboration with COMBINEDBrain was able to organize a multi-state mobile phlebotomy roadshow last Fall where blood samples were collected from three FAM-affected families, two affected siblings per family. Healthy controls (parents and unaffected siblings) also volunteered samples. In total, 15 samples — 6 FAM affected plus 9 healthy controls — were shipped to SomaLogic for processing on their SomaScan platform, which precisely measures the levels of thousands of serum proteins.
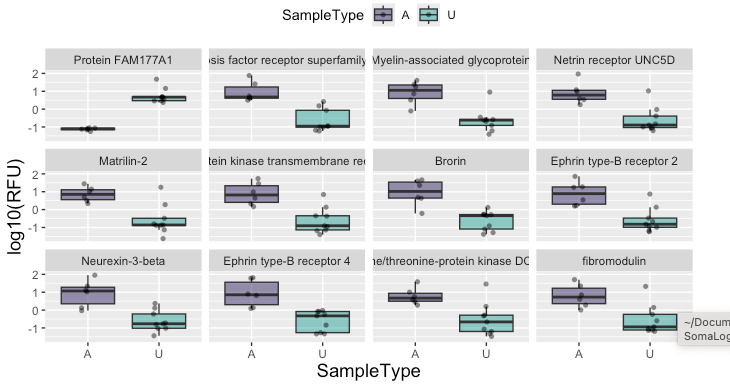
The samples were processed over the winter. Last month, SomaLogic delivered the data package. Perlara Cure Guide Dr. Arun Ramani performed a preliminary analysis. As a sanity check, Arun examined the levels of the FAM177A1 protein itself. FAM patients are by definition homozygous for loss-of-function mutations, including large deletions which render a nonfunctional truncated protein or no protein at all due to nonsense-mediated decay.
So the expectation was that FAM177A1 protein levels would be significantly reduced in FAM patients compared to controls. This is indeed the case, as shown above. The level of FAM177A1 protein in the sera of six FAM patients is at the lower limit of detection compared robust expression in all control samples. The false discovery rate (FDR) corrected p-value is 0.00031.
Including FAM177A1, there are 12 proteins whose mean expression levels are different in FAM patients relative to healthy controls:
FAM177A1 is the only protein whose expression is lower in FAM patients versus healthy controls. In the 11 other cases of differentially expressed proteins, expression is higher in FAM patients versus healthy controls. However, none of those 11 hits reached statistical significance given the small sample sizes. The eleven proteins are:
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 21 (TNFRSF21)
Myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG)
Netrin receptor UNC5D (UNC5D)
Matrilin-2 (MATN2)
Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 (ROR2)
Brorin (VWC2)
Ephrin type-B receptor 2 (EPHB2)
Neurexin-3-beta (NRXN3)
Ephrin type-B receptor 4 (EPHB4)
Serine/threonine-protein kinase DCLK1 (DCLK1)
Fibromodulin (FMOD)
If any of the proteins on the above hit list ring a bell, please reach out. Perlara Cure Guide Helen Hernandez did some initial detective work keeping in mind that we’re still dealing with trends toward significance and a small sample size of six FAM patients ranging in age from 4 to 18.
The hit list implicates vascular development, inflammation and apoptosis. RNAseq data is publicly available from FAM patient-derived PBMCs and fibroblasts, as well as a FAM deficiency zebrafish model. We’re conducting a preliminary meta-analysis. In parallel, we await hit validation data from the FAM fly repurposing screen. We’re working as diligently as we can to find convergences across datasets and models.